
By James Kwantes
Resource Opportunities
North Arrow Minerals is one of three Resource Opportunities sponsors and Lucara Diamond and North Arrow are portfolio companies.
Canada punches above its weight in the world of diamonds – way above. Consider: the country is home to about 36 million people, or less than half of one percent of the world’s population. Yet in 2017, Canada produced 14% of the world’s diamonds by value, behind only Russia and Botswana.

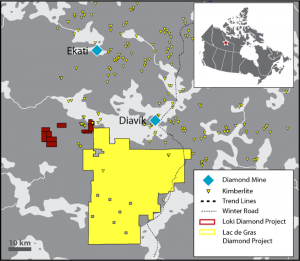
The epicenter of Canadian diamond production lies in the frozen tundra of Canada’s North – the “Barren Lands,” in author Kevin Krajick’s words. Specifically, the Lac de Gras region, 300 kilometres northeast of Yellowknife, the Northwest Territories’ capital city. That’s where prospectors Chuck Fipke and Stu Blusson discovered the kimberlite indicator minerals that let to Dia Met’s 1991 diamond discovery. When Ekati went into production in 1998, it marked the birth of what has become an important northern industry.
The discovery of the Diavik diamond mine by Gren Thomas’s Aber Resources in 1994 established that the Ekati find was no fluke. Diavik went into production in 2003 and quickly became one of the world’s richest diamond mines. The discovery of diamonds in this inhospitable corner of the world, surrounded by only frozen lakes and tundra, is a testament to the ingenuity and perseverance of Canada’s diamond pioneers.
Two decades later, the Ekati and Diavik diamond mines are still churning out carats – and cash. More than $20 billion worth of diamonds has been mined at the two operations. The prized profit centers didn’t escape the notice of the Washington Group, a private conglomerate founded by US billionaire Dennis Washington. Last year the Washington Group paid about US$1.2 billion to snap up Dominion Diamond Corp., owner of a controlling 90% interest in Ekati and a 40% stake in Diavik (operator Rio Tinto owns 60%).

CANADA’S GROUND ZERO FOR DIAMONDS
And the Lac de Gras region remains a hub of activity for diamond production and exploration, well beyond Ekati and Diavik. The newest mine is Gahcho Kue, which began commercial production in March 2017 and is 51% owned by De Beers and 49% by Mountain Province Diamonds (MPV-T).
North Arrow Minerals (NAR-V), Canada’s most active diamond exploreco, is also zeroing in on Lac de Gras. The company has two projects in the region and both of them will see drilling this spring. The Loki project covers 8,600 hectares and is close to both Ekati (33 km away) and Diavik (24 km). North Arrow will drill about 1,000 metres on up to six targets in March.
Loki is a good example of a junior company benefiting from millions of dollars spent by a major while big money flowed into exploration. One of the six Loki targets is EG05, a diamondiferous kimberlite that Rio Tinto (Kennecott) discovered but never followed up on. The other targets were identified through airborne geophysics and electromagnetic surveys. At each target, pyrope garnets and other kimberlite indicator minerals have been recovered, but no source has been found.
At Dominion’s Lac de Gras (LDG) joint venture with North Arrow, operator Dominion is ramping up for 2018 exploration, including spring drilling. Dominion has an approximate 67% interest in LDG, with North Arrow retaining 33%. The LDG JV covers a vast 125,000-hectare property to the south of the Ekati and Diavik mines and immediately east of Loki.
The “privatization” of Dominion Diamond Corp. translates into fewer eyes on the company, particularly its exploration initiatives. But Patrick Evans, Dominion’s CEO – appointed after the takeover – is well-known in the diamond world. Evans is the former president and CEO of both producer Mountain Province Diamonds (MPV-T) and explorer Kennady Diamonds (which was recently taken over by Mountain Province for $176 million).
DRIVE FOR DISCOVERY
Evans’ exploration background – and his assertion that new diamond discoveries are critical to the viability of the Canadian diamond industry – will likely ensure that exploration remains a key focus for Dominion. In a 2016 talk at the annual Roundup Mineral Exploration conference in Vancouver, Evans lamented the “paltry” amount being spent on diamond exploration in Canada. The dearth of exploration threatens Canada’s No. 3 position as a world diamond player, Evans said at the time.
Loki and the LDG joint venture represent North Arrow’s most imminent potential catalysts. But North Arrow continues to advance its flagship Naujaat coloured diamond project in Nunavut, which has a population of rare, valuable fancy yellow diamonds.
On Wednesday the company announced it had recovered 64.25 carats from a 209.8-tonne mini bulk sample collected last year from three phases of the large Q1-4 kimberlite. The proportion of the more valuable yellow diamonds was consistent with an earlier bulk sample – 10.7% of the total by stone count and 21.2% by carat weight.
“It’s encouraging, because it confirms the yellow diamond population exists in different phases of the kimberlite,” said North Arrow CEO Ken Armstrong, noting that the results merit further work. “The size of the prize is large.”
The next step, Armstrong says, is a large bulk sample at Naujaat – perhaps as large as 5,000 to 10,000 tonnes. A sample of that size would answer remaining questions about the value of the diamonds and size-frequency distribution of the yellow stones, he said. It would also carry a large price tag: perhaps between $20 million and $30 million. Securing a joint venture partner would allow North Arrow to undertake the bulk sample without blowing out the share structure, Armstrong pointed out.

The diamond sector has faced some ups and downs in recent years, but mostly downs. One of the main issues has been large inventories held by industry heavyweights Alrosa and De Beers, which has suppressed rough diamond prices. There have been some high-profile scandals in the sector, too – Indian diamond magnate Nirav Modi fled India earlier this year and is currently being investigated for alleged bank fraud and money laundering.
However, the macro picture is improving, according to New York diamond analyst Paul Zimnisky. Inventory levels for both De Beers and Alrosa are at estimated three-year lows and demand remains healthy, according to Zimnisky’s latest State of the Diamond Market report. On the supply side, no new mines are coming onstream in 2018 and Alrosa’s production is forecast to decrease this year.
For a sector that has struggled – and been bypassed by many retail investors – there’s a lot going on. The takeover of Dominion Diamond by a private group was a surprise to many; less so the purchase of Kennady Diamonds by Mountain Province, which had earlier spun out the exploreco. There are new and rejuvenated exploration plays, including Bruce Counts’s newly listed Lithoquest Diamonds (LDI-V) with its North Kimberley project in Australia. In the Northwest Territories, GGL Resources (GGL-V) has revamped with the appointment of 25-year diamond veteran David Kelsch as CEO and an injection of capital from project generator Strategic Metals.
ENTER EIRA
But for diamond sector investors, perhaps the most interesting moves were made by Lucara Diamond Corp. (LUC-T) on February 25. Diamond veteran Eira Thomas was named Lucara’s CEO and the Vancouver-based company announced a blockchain initiative that could improve transparency and efficiencies in the sale of diamonds in the one to 15-carat range, and eventually for smaller stones as well. Blockchain will not be used to sell the larger diamonds that have established Lucara’s reputation and bolstered its treasury – stones such as the 1,109-carat Lesedi La Rona and 813-carat Constellation.
Eira’s most recent CEO gig was with Kaminak Gold, which was sold for $520 million to Goldcorp in 2016. Before that, Eira – the daughter of North Arrow chairman Gren Thomas – cofounded Stornoway Diamond Corp. (SWY-T) and Lucara. Her partner on both initiatives was Catherine McLeod-Seltzer, who is joining Lucara’s board of directors. The appointments mark a kind of reunion for Lucara’s three co-founders – Thomas, McLeod-Seltzer and Lukas Lundin.

But before Stornoway, Lucara or Kaminak was Aber Resources. Hired as an Aber field geologist straight out of university, Eira was thrust into a lead role when a senior geologist left for another company. In the spring of 1994, the geologist and her exploration team raced the spring melt and drilled one final hole from a floating ice platform. The core had a 2-carat diamond embedded in it, and the rest is history. She later became VP Exploration for Aber, Dominion Diamond’s predecessor company.
Eira’s appointment as Lucara CEO strengthens already solid connections between Lucara and North Arrow. She remains a North Arrow advisor and large shareholder, and was critical in landing $2-million investments from both Ross Beaty and the Electrum Strategic Opportunities Fund L.P., which is funding North Arrow’s current programs. There’s a brother connection between the two companies, too – North Arrow CEO Ken Armstrong’s brother John is Lucara’s vice-president, mineral resources. His specialty is the assessment and analysis of diamond size and value distribution as well as deposit modelling. John Armstrong’s partner Allison Rippin Armstrong, a corporate social responsibility specialist, is an advisor to North Arrow.
As for Eira, her association to North Arrow’s flagship Naujaat project runs deep. It was Thomas who secured the Naujaat project (formerly called Qilalugaq) from Stornoway Diamonds and brought it to North Arrow, after stepping down as Stornoway’s executive chairman. The Naujaat, Pikoo and Timiskaming projects were optioned from Stornoway on a JV basis, with North Arrow subsequently buying out Stornoway’s stakes to secure 100% interests in Naujaat and Pikoo.

Assays are pending for 2,440 metres of kimberlite core drilled at Naujaat last fall. Further drilling later this spring will conclude the program at the 12.5-hectare kimberlite, the largest in the Eastern Arctic. Naujaat has an Inferred mineral resource of 26.1 million carats from 48.8 million tonnes grading 53.6 carats per hundred tonnes, from surface to 205 metres depth. Fall drilling established that Q1-4 remains open at depth and has a surface area of at least five hectares 305 metres below surface.
Further north, there are also drill plans at Mel, North Arrow’s second grassroots discovery of a diamondiferous kimberlite field in Canada (Pikoo was the first). In October, North Arrow announced the recovery of 23 diamonds larger than the .106-mm sieve size from a 62.1-kilogram sample at the ML-8 kimberlite. The diamond body was discovered through the systematic tracking of a kimberlite indicator mineral (KIM) train to its up-ice termination. North Arrow has subsequently increased its Mel land position to 56,000 hectares through staking. Driling will focus on ML-8 as well as other targets at the heads of three well-defined KIM trains.
Disclosure: North Arrow Minerals is one of three company sponsors of Resource Opportunities and James Kwantes owns North Arrow and Lucara shares, which makes him biased. Readers are advised that this article is solely for information purposes. Readers are encouraged to always conduct their own research and due diligence, and/or obtain professional investment advice. Dollar and $ refer to Canadian dollars, unless otherwise stated.


 James Kwantes is the editor of Resource Opportunities, a subscriber supported junior mining investment publication. Mr. Kwantes has two decades of journalism experience and was the mining reporter at the Vancouver Sun. Twitter:
James Kwantes is the editor of Resource Opportunities, a subscriber supported junior mining investment publication. Mr. Kwantes has two decades of journalism experience and was the mining reporter at the Vancouver Sun. Twitter:  Resource Opportunities (R.O.) is an investment newsletter founded by geologist Lawrence Roulston in 1998. The publication focuses on identifying early stage mining and energy companies with the potential for outsized returns, and the R.O. team has identified over 30 companies that went on to increase in value by at least 500%. Professional investors, corporate managers, brokers and retail investors subscribe to R.O. and receive a minimum of 20 issues per year. Twitter:
Resource Opportunities (R.O.) is an investment newsletter founded by geologist Lawrence Roulston in 1998. The publication focuses on identifying early stage mining and energy companies with the potential for outsized returns, and the R.O. team has identified over 30 companies that went on to increase in value by at least 500%. Professional investors, corporate managers, brokers and retail investors subscribe to R.O. and receive a minimum of 20 issues per year. Twitter: 
